Features Overview
But before moving on to a detailed consideration of these materials, you need to understand what the main environmental characteristics are.
There are many manuals and techniques in which the authors see them in their own way. However, in general, it is customary to distinguish 4 such basic characteristics. OSB, like plywood, is an environmentally friendly product because it is made from chips of various trees.
- Fire safety. As a rule, there are several fire safety categories of group “G” from 1 to 4 or 5, depending on the methodology. And the higher the number, the greater the risk of fire. So, plywood products used for the construction of entire or parts of indoor floors must have category G1 - that is, optimal safety. When constructing a wooden building, the fire safety of the materials used must be at least level G2.
- Physical security. Here, such basic coefficients as thermal conductivity and thermal resistance are of greatest importance. They must be within acceptable values. This suggests that plywood products for finishing residential premises should not accumulate charges, absorb sounds well, and also not create sound vibrations and various types of frequencies harmful to the body.
- Biological safety implies the use of impregnations against fungi and pests with compositions that will not harm human health. Due to the fact that today there are many impregnations that have a certain degree of toxicity, this indicator cannot be neglected.
- Chemical safety is another fairly important indicator of plywood materials. This is where the MPC (maximum permissible concentration) indicator comes into play. It concerns substances and volatile materials released into the air. As a rule, each substance has its own permissible concentration according to safety standards. And in this case it should not be exceeded. This applies to poisonous and toxic substances in general. Of course, ideally they should not stand out at all in a living space. But if this cannot be avoided in any way, then it is necessary to at least minimally follow these concentration standards.
These were the main environmental indicators of products based on plywood and chips. Taking into account these four parameters together will protect you from the wrong choice, which can cause significant harm to your health. Now let’s look separately at the characteristics of OSB and plywood in this regard.
Environmental friendliness
In the manufacture of wood composites, binders based on formaldehyde resins are used. These resins, even after the completion of the technological process, continue to emit volatile formaldehyde, which is harmful to health. All composite materials of this type are divided into classes according to the intensity of formaldehyde emission. The lower the class, the safer the stove, regardless of its type.
All discussions about where there is more resin and where there is less, which is better, chipboard or OSB in this regard, are broken down by the GOST numbers.
- If the formaldehyde content is not higher than 4 mg per 100 g of dry material, the board belongs to class E0.5.
- With a content of 4 to 8 mg/100 g, the material has class E1.
- Up to 20 mg/100 g – class E2.
These figures are the same for both materials, which means choosing the degree of environmental friendliness comes down to choosing the desired emission class. Materials of class E2 are prohibited from being used in residential premises. Classes E1 and E0.5 are approved for the production of furniture, the manufacture of any structures and cladding in residential premises.
In terms of environmental friendliness, chipboards and oriented strand boards do not differ from each other.
Comparison of characteristics
To choose the most suitable option for rough or fine finishing of a floor structure, it is necessary to take into account the main parameters of the product.
Environmental friendliness
Health safety is one of the main factors. The indicators of wood-based panel materials comply with the standards reflected in standardization documents.
- Plywood. Eco-friendly option. The most harmless products are those that are glued using natural resins.
- OSB. It does not pose a threat, but only if the production technology is followed. It is better to choose trusted manufacturers.
- Chipboard. This variety causes the most controversy regarding health hazards, since formaldehyde resins are used for gluing. Products must comply with standards (marking E1 or E0.5).
- Fiberboard. Does not pose a threat provided that high-quality raw materials are used.
- MDF. Eco-friendly material made using urea resins. These products must also comply with class E1 or E0.5.
Since the outside of all materials is finished, harmful fumes are minimized.
Strength
To choose the most reliable option, you need to take into account the density and structure of the product:
- OSB and plywood. Oriented strand panels can withstand heavy loads well: the layers are placed in different directions and glued together extremely firmly. But wood-laminated board may have a significant disadvantage - the possibility of deformation due to non-compliance with the technology.
- Chipboard and fibreboard. They have sufficient hardness. Their areas of use are somewhat different. Wood-shaving parts are thick, and wood-fiber parts are very unstable in bending, so they cannot be used for leveling voids.
- MDF. A relatively soft material that is not used in places with high loads.
It is difficult to compare all products on this parameter, since they have different sizes.
Dimensions
The length and width of all varieties are approximately the same, so it is necessary to compare the thickness:
- Hardboard. The thinnest material. Its thickness can reach up to 7 mm, but the most common is 3.2 mm.
- Plywood. For the floor, products with a thickness of 12–15 mm are selected.
- OSB. Can be of different sizes, but for flooring options from 10 to 22 mm are used. If you need to level the existing base, then a thickness of 1 cm is suitable, but in order to lay the material on wooden logs, the parts must be more durable.
- MDF. Due to their softness, the recommended thickness of the slabs varies from 18 to 25 mm.
- Chipboard. For horizontal structures with increased load, a tongue-and-groove version with a thickness of 16–22 mm is used.
The thickness and structure of the parts also affects protection from sound penetration and heat retention. If the noise pollution is very strong, then it is recommended to give preference to medium-density fiberboards of maximum thickness. They also serve as additional thermal insulation, which is similar to OSB.
Price
The difference in the price of materials depends on many factors: production method, raw materials used, additional processing, size and even place of sale.
- The most expensive is high-grade plywood.
- The cost of MDF is calculated per square meter and depends on the manufacturing method.
- The price of OSB-3 and 2 corresponds to wood-laminated boards of grade 3 or 2 of a smaller size.
- The lightest and cheapest option is fiberboard.
To ensure that the total work budget does not amount to too significant an amount, it is necessary to immediately determine the scope of application of each type of product.
Easy to install
Laying wood boards is not difficult; it does not require professional skills or complex tools. The order of work depends on the specific situation:
- If a frame structure is being erected, then OSB would be the best option.
- The light weight and thickness of hardboard make processing the fastest, but it is not suitable for serious leveling.
- Chipboard and OSB panels are cut and fixed almost identically. They are much easier to trim than MDF, which due to its dense structure offers more resistance.
- The most labor-intensive material to process is plywood. It will take much longer to place the product. It is more difficult to drill or adjust to size due to the presence of layers of natural wood in the structure.
All floor slabs are mounted on glue or joists, the only exception is the fiberboard covering: these sheets are not intended for laying on joists, they need a flat and durable base
OSB, plywood, chipboard - what's the difference?
In construction work today, the use of cheaper and more modern wood substitutes such as OSB, chipboard and plywood is widespread. The method of their manufacture is largely similar, therefore a number of characteristics of these materials are identical. At the same time, they also have significant differences, which determine the advantage of their use in a particular case.
Plywood
This material is made from three or more layers of veneer, which are joined together using a special glue. The performance properties of plywood are influenced by the fact that its individual layers can be made from birch or coniferous wood. A design feature of the material is the perpendicular laying of each subsequent sheet. The main advantages of plywood are its moisture resistance, aesthetics, and ability to recover after slight wetting. At the same time, prolonged exposure to moisture can contribute not only to the swelling of the material, but also to its rotting, and the formaldehyde resins used to glue the layers have a negative impact on the environmental friendliness of housing.
Chipboard
Stroywse.ru recommends purchasing chipboards (chipboards) for cladding walls, constructing partitions or arranging a base for flooring. In addition, this material is actively used in the production of furniture; in this case, preference should be given to laminated boards. Chipboard is made by pressing wood chips at high temperatures, using a binder for bonding. The resulting material has high sound and heat insulation, is easy to process, does not rot, and has a low price. However, chipboard is susceptible to moisture and has less strength than OSB or plywood.
OSB
On the construction market, OSB board is a fairly new product. When producing this material, the outer flat wood chips are arranged longitudinally, and the inner ones - crosswise. Thanks to this, OSB is highly durable, and a number of its types are also used in rooms with high humidity. This material is optimal for the construction of frame houses and low-rise construction, as it allows not only to save on the construction of the foundation, but also to significantly reduce construction time. In addition, OSB is considered more environmentally friendly, since its production today uses 10 times less harmful substances than in the production of chipboard or plywood.
www.realto.ru
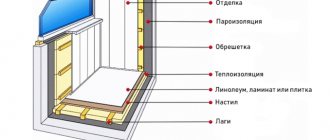
Technology for constructing a subfloor from sheet materials
Sheet materials can be laid on old coverings (plank floors, linoleum), on screed-leveled floors or on joists. In the first two cases, in addition to fastening with screws, glue is used.
Flooring on screed
A cement screed is used to level the surface. To do this, using a level, a line is drawn on the walls along the perimeter of the room, which will serve as a guide for the height of the screed.
Then bars are laid on the base, forming a grid of squares with a side length of about 1 meter. Their thickness should be slightly less than the thickness of the future screed.
Next, a cement-sand mortar is prepared in a ratio of 1:3, which is poured into the mesh cells and smoothed.
Leveling screed device
Note. To prevent the screed from cracking, it is necessary to ensure that a certain level of humidity is maintained during drying.
To do this, cover it with plastic wrap and leave it for 7-10 days.
After the solution has dried, the instructions require priming the surface with bitumen mastic and letting it dry. After this, you can begin laying the subfloor.
We advise you to study - How to wash windows correctly and without streaksThe sheets are laid on a surface greased with glue with a slight indentation from the walls and with a gap between them of 2-3 mm, necessary for temperature and humidity expansion. They should be laid out with offset joints: the corners of four sheets should not meet at one point.
Chipboard fastening
After laying the chipboard or plywood on the floor, it is drilled and screwed to the base, first in the center, then along the perimeter.
Laying on joists
This method is less labor-intensive and more environmentally friendly. If necessary, insulation or soundproofing material is laid between the joists.
Floor insulation
However, thicker and stronger sheets must be placed on the joists to avoid their deformation. What is stronger - chipboard or plywood? This depends on the thickness of the sheet and the distance between the joists.
For example, 12 mm plywood can be placed on a solid base, and at least 20 mm on logs, provided that the distance between them is no more than 40 cm. The thickness of the chipboard should also be 18-22 mm.
- Draw a diagram for laying the joists depending on the size of the sheet material (see also the article Plywood flooring on joists - a simple technology that requires a thoughtful approach). The joints of the sheets should be on the center lines of the joists. In this case, take into account the shift of the sheets to offset the seams. You should end up with a mesh with a cell size of 30-50 cm.
- Lay longitudinal joists on the floor and level them using spacers. Secure.
Attention! The distance between the wall and the outer joists should be no more than 30-40 mm
- Mark the position of the transverse joists and attach them to the longitudinal ones with nails driven in diagonally.
Photo of the finished frame
- Place the first sheet in the corner of the room, retreating from the walls by 10-15 mm. To avoid straying from the center line when attaching to intermediate joists, apply pencil marks to the edges of the sheet corresponding to the middle of the bars and connect them with a straight line. Screw in the self-tapping screws along these lines in increments of 100-150 mm, recessing the caps into the body of the material. Then secure the sheet around the perimeter. It is best to use an electric screwdriver.
- Mount the remaining sheets in the same way, leaving a gap of 2-3 mm between them. If it is not there, the floors may begin to creak over time.
Attaching sheets to joists
- When using tongue and groove sheets, there is no need to leave a gap. In this case, the tongue and groove joints are lubricated with glue and compacted by tapping each other with a mallet.
- Remember to offset the sheets to prevent the four seams from intersecting at one point, and to leave a gap between them and the wall. Subsequently, they will be covered with a plinth.
It remains to be said that when laying in rooms where increased humidity is possible, sheet materials must be covered with drying oil or other protective agents before laying. If the room is dry, then from the point of view of cost savings and ease of processing, chipboard for the floor is better than plywood.
What material is better for the floor?
To select the most suitable option, the specifics of the room and the final coating are taken into account:
- Under the tiles in the bathroom you can use chipboard and OSB, but only varieties with moisture-resistant impregnation. If you place products without treatment, there is a high probability of mold and mildew. This also applies to the decoration of the kitchen, hallway and balcony.
When arranging a subfloor under tiles or other finished floor covering, one of the best options is the use of moisture-resistant OSB or chipboard boards - Old wooden bases, prepared in advance and without serious defects, can be leveled with hardboard by laying it directly on the boards.
- When installing “dry” screeds, preference is given to plywood and chipboards.
- If the house does not have a solid foundation, then OSB is hemmed along the joists on both sides. Another option is the simultaneous use of plywood and OSB.
- To level the floor under the laminate, you can use fiberboard. But if you need to create a rigid base, it is better to lay plywood and OSB.
Thus, it is impossible to single out any one material. To obtain better results and increase the service life of the coating, it is preferable to combine products.
Comparison of both materials
If we try to determine the differences between these two materials, then, in addition to the production method and performance characteristics, we can highlight the following:
- The basic price tag of plywood exceeds the cost of average quality OSB. However, heavy-duty and luxury grades of OSB can be more expensive than plywood. Manufacturers justify this fact by the fact that the chip material uses expensive impregnations, varnishes and decorating additives. At the same time, decorative varieties of plywood significantly exceed the cost of OSB with average strength indicators.
- The structure of the OSB board is represented by 4 layers, and as for plywood, the number of veneer layers is not limited, thereby increasing the strength of the product.
If you compare the properties of OSB, plywood and chipboard, which is better is difficult to immediately understand. If you need a lightweight and affordable material, choose OSB; in cases where the budget is very limited, use chipboard. However, remember that the edges of this material may break off over time. If strength is your first priority, it is better to choose plywood. But this option will be the most expensive.
How to choose
The construction of frame houses for any purpose requires a serious approach to the choice of DSP and OSB
When purchasing, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Manufacturer of slabs.
- Sheet size.
- Sheet thickness.
- Compound.
- Appearance: evenness, uniformity of texture, absence of voids and knots.
- Storage conditions.
The relatively low cost of DSP and OSB boards with decent technical characteristics makes them very popular as cladding for frame houses.
Building a house using frame technology promises many benefits to the future owner of the house. Such a house is built much faster than traditional brick or wooden houses. It does not require a powerful foundation, since it has significantly less weight, and with the right choice of materials it also allows you to save on interior and exterior decoration. However, if construction technology is violated, all the advantages of a frame house instantly turn into disadvantages. How to avoid this? There are a few trivial things that you shouldn’t forget:
- Build a house according to the project. Having a project linked to the area, with a pre-calculated estimate, and linking all communications on the site has never harmed construction.
- An experienced team is always better than covens. And having an agreement listing all the main responsibilities and stipulated responsibility for failure to complete the work will undoubtedly add confidence in the final result.
- Use of quality materials. A dry calibrated board as a frame is significantly superior to other lumber. Of course, there is always a desire to save money, but this is exactly the case where saving can lead to large losses in the future.
- Use suitable materials for insulation and sheathing. The insulation can be polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, basalt or mineral wool, ecowool, etc. The cladding can be made of OSB, DSP, Plywood and even edged boards.
Let's look at the last point in more detail. Plywood is an excellent material for building frame houses, and if it were not for its price, frame houses would be built primarily from plywood. The cost of covering a house with plywood will be about a third higher than the cost of OSB or DSP. Edged boards require a large amount of manual labor: planing, drying, fitting, and so on. Therefore, construction may take a long time. But DSP and OSB wood boards do not have these disadvantages. Let's talk about them in more detail.
What are the advantages of plywood over OSB?
In short, one of the big advantages of plywood over OSB is that the higher the drying ability of a wall, the more durable it is, and everyone agrees that more moisture will pass through plywood. This is not a recommendation to never use OSB, but it is a reason to consider all the variables and make sure that all the components of your wall will not trap moisture inside.
Project for finishing a living space with plywood
Application in frame walls - OSB vs plywood:
For better or worse, the market has stepped up and provided many additional solutions to meet these demands; for example, rigid insulation with membranes attached, or sheathing with foam insulation attached, as shown in the picture above of the corner of a house under construction.
“Some rigid insulation products, such as extruded polystyrene, are also relatively impermeable to vapors
When using them, care must be taken in selecting the facing material to ensure that significant amounts of water do not reach the interface between the extruded polystyrene insulation and the vapor permeable membrane shell. This risk may dictate the use of insulation products with high vapor permeability and low water retention, such as mineral fibers
Where to install a vapor barrier:
“Materials that act as vapor barriers, including certain types of insulation, must be located within the structure so that moisture moving from the inside to the outside does not condense and accumulate within the assembly. This means that the vapor barrier should be located on the warm side of the insulation materials.
With all the conflicting findings from credible researchers, we wanted to take into account this basic law of physics—warm, moist air condenses and leaves moisture on cooler surfaces. Anyone who's ever held a cold drink on a hot day knows this. So, if you keep heat on a condensing surface, you reduce the risk of moisture buildup.
We advise you to study - Which wallpaper to choose for the bedroom from all their variety. how to choose the right wallpaper for the bedroom
Today, in this advanced world of software modeling, the "old two-thirds rule" still makes sense, which involves applying 2/3 of the total volume of insulation to the exterior wall, a formula that has been tested and meets all its stated specifications. This keeps the home warm and there is no doubt that it reduces the likelihood of condensation forming inside the walls. And if you're sticking a large amount of rock wool onto an exterior wall that allows vapor to pass through, the whole mess of estimating all the processes becomes a moot point.
Which is stronger: OSB or plywood?
Generally speaking, plywood of the same thickness bends slightly less than OSB. For use on the floor, this characteristic is important. Strength is assessed by bending along and across the long side of the material.
- Longitudinal bending strength: OSB 3 - 16 to 22 MPa;
- FSF - 25-60 MPa.
- OSB 3 - 10-18 MPa;
- OSB 3 - 0.34-0.13 N/sq. mm;
Plywood differs from OSB in the production method.
Strength measurements are also carried out after “soaking” the materials. In OSB, the indicator drops by almost half (so the bending was not too high and has also decreased significantly). With plywood it is practically unchanged both when wet and after drying. So the choice in terms of strength between plywood and OSB is clear: plywood is stronger. But the data is given for coniferous plywood of the FSF brand - it is the most moisture-resistant and practically the most durable of all.
Laying technology
The installation process does not require special knowledge or talent, so even a beginner can handle this work. OSB, chipboard or plywood is laid on the floor in two ways - on a flat surface and on logs. The first option requires the presence of the most durable and even base, which can be either a regular screed or a boardwalk. The floors must be clean so that nothing interferes with the adhesion of the glue to the base.
The second option is more labor-intensive, but it allows not only to level the surface, but also to efficiently insulate the underground space. Preliminary measurements of the area are carried out so that plywood and OSB, the dimensions of which are slightly different, are laid with a minimum number of joints.
To install the slabs on the screed you will need:
- roulette;
- level;
- a circular saw;
- OSB sheets;
- primer;
- notched spatula;
- dowels;
- rubber based adhesive.
First, the screed plane is checked with a level to eliminate differences in height. Next, chipboard or OSB is laid out on a dry surface and cut lines are marked for precise fitting of the sheets. After cutting, cover the back side with glue and place it in pre-marked places. Press firmly with your hands to the floor, be sure to check the horizontal level with a level. Plywood (OSB) is laid on the floor quite quickly, so the work will not take much time.
When installing USB, a gap of 10-15 mm wide should be left around the perimeter of the room and seams 3-4 mm wide between the plates themselves. This is necessary to compensate for material deformations due to changes in humidity and temperature conditions. After installation is complete, you need to wait for the glue to dry and additionally secure the flooring with dowels. They are screwed into pre-drilled holes in the corners of each slab.
OSB or plywood is installed on a wooden floor in a similar way. The base must be strong and level, without serious defects. If there are large gaps or the board bends under your feet, you first need to fix the problem and only then begin installing the sheets. In this case, OSB can be laid on the floor without glue, using only wood screws for fastening. The latter are screwed in increments of 20-30 cm around the perimeter of each slab.
To lay the floor along the joists, you will need:
- strong timber with a section of 100x150 mm;
- OSB sheets;
- level and tape measure;
- self-tapping screws;
- anchors;
- screwdriver
It should be noted that the choice of sheet thickness depends on the distance between the logs: with a step of 40 cm, the minimum thickness is 15 mm, with a step of 50 cm - 18 mm, with a step of 60 cm - no less than 22 mm. The logs are laid on the floor, which is best done with an assistant, and set strictly according to the level. Next, holes are drilled for the anchors and the timber is secured to prevent it from moving.
Clean sheets are tried on and cut out, after which they are laid on top of the joists, with the seams obligatory to be shifted in each subsequent row. The flooring is fixed with self-tapping screws every 15 cm around the perimeter of the sheets and at a distance of 10-15 mm from the edge. This is how plywood or OSB is simply laid on the floor, after which the finishing coating is laid.
Installation subtleties
The type of decorative finish is taken into account: painting, linoleum, parquet, laminate. In the first case, plywood is used. For comparison, OSB loses its attractiveness when paint is applied; it is better to coat such sheets with varnish or choose another coating (laminate, linoleum). Both types (plywood, OSB) are equally often used for attaching a rough base.
You should use as many solid sheets as possible when installing the covering. Strength will depend on this. Moreover, the type of base is different: concrete, logs, plank base. In each case there are a number of installation features.
Concrete base
The sheets are laid on a flat surface. The 8 mm option will do. Dowels are used to fix OSB and plywood, since it is important to ensure the strength of the fastening in concrete. To strengthen the structure, it is recommended to first apply an adhesive composition to the floor.
On the logs
The minimum thickness of the slabs is 22 mm. Provide a distance between the bars of no more than 50 cm. To reduce the risk of sheet deflection in the voids (cells between the logs), bars are used. In this case, you need to fasten the wood with self-tapping screws. Glue is an unreliable method of fixation when installing a wooden floor on joists.
Board covering
Fastening method: self-tapping screws. Leave 1 cm along the walls. These areas will be sealed in the future. The recommended pitch when using self-tapping screws is 15 cm (for plywood) and 30 cm (for OSB). You can use material 12 mm thick. Moreover, it should be laid so that the joints are staggered.
Difference between plywood and OSB
OSB and plywood offer similar (and sufficient) performance in terms of strength and functionality, although plywood is 7% stronger. The main difference between them is how they handle moisture, and surprisingly there are quite varied conclusions - from very reputable sources - as to how breathable they are. We don't do any internal testing, so all we can do is report others' findings. In the absence of consensus among researchers, we will start with the general conclusions that all parties agree on - plywood is more permeable to vapors than OSB.
Project of finished room decoration from OSB
Plywood absorbs moisture faster than OSB, but therefore it also dries faster. Both products will swell when wet, but when dry, the plywood will return to almost its exact shape. OSB is less likely to be left out in the rain and will show more deformation after wetting and drying.
In addition to concerns about moisture exposure during construction, there is moisture that can penetrate wall assemblies after completion. How durable a wall is depends largely on its ability to dry, and how well it can dry depends on the materials you choose to build the wall.
Preparation
If you set out to get a perfectly flat floor, you should first lay the joists. However, careful horizontal leveling may not be required; in this case, it is necessary to check how suitable the floor is for further use.
The plank floor must first be cleaned of old coating, debris and dust. After which you can proceed to checking the boards for strength; they should not be damaged or creak under mechanical stress; this can especially occur near doorways.
Technological diagram of the production process in the manufacture of plywood.
You can strengthen the floors in places where there are creaks with nails, the length of which is 150 mm. If the boards are deformed or show signs of rot, they will need to be dismantled and then replaced with new ones.
OSB, plywood or chipboard must be laid to ensure a temperature gap between adjacent sheets, as well as canvases and walls. The step from the wall to the subfloor slab can reach 20 mm, which can then be covered with plinths and decorative coverings.
When laying OSB on logs, you should create a temperature gap around the slab, the minimum width of which is 3 mm. But the wall should be 12 mm away from the slab, which is true when installing floors using floating technology.
Plywood is also subject to deformation caused by temperature changes, and if the sheets are laid too tightly, you can get squeaks. You can eliminate unpleasant consequences by laying plywood with a gap between the sheets of 5-10 mm.
The distance from the walls to the plywood sheets should be 10-20 mm. The plywood must be cut first, during which a hacksaw should be used, which has fine teeth. After making the cut, apply masking tape to the cut site. Before installation, the slabs must be treated with drying oil.
In the case of chipboard, the temperature gap should be 10 mm.
We advise you to study - Rating of metal entrance doors
If you still can’t make your choice - plywood or OSB, then you should take into account that plywood is easier to saw, but in the places where OSB is cut, you should also stick tape to prevent the fibers from peeling off.
Plywood and chipboard, like OSB, can be sawn with a jigsaw or fine-toothed saws. The plywood must be sawn along the grain, and then the cuts can be processed with a plane; it is preferable to use an end tool for this. Then you can sand the cut until it becomes shiny. Plywood may be of low quality; in this case, its slabs have delaminating fibers. In order to arrange the floors, you should choose high-quality material.
Fiberboard (Fibreboard)
Fibreboards are the main sheet material used in a wide variety of floor designs. Fiberboard is made practically from wood waste using the hot pressing method. Fiberboard is not afraid of moisture, adheres well and partially absorbs sound.
If you look at the technological maps and regulatory documents on the construction of floors, fiberboard remains the main sheet material used in the construction of screeds.
However, the small thickness of the sheets limits their use in prefabricated screeds on joists, leaving them a niche for prefabricated screeds on the backfill or use as a substrate.
Fibreboard laying
- Fibreboard is laid on hot or cold mastic with 40% of the surface coated in two layers. The seams between fiberboard sheets (without a lock) must be glued with paper or tape 50±10 mm wide.
- Rolled finishing materials (linoleum, carpet) are laid on super-hard fiberboard sheets. Fiberboard strips serve as a layer between the floor joists and the concrete.
Comparison by characteristics
Most often, either plywood or OSB is placed on the floor. But what's better? Most will say that plywood is stronger in bending and therefore it is better to lay it on the floor. It's stronger. That's for sure. But if the material is laid on a concrete base, or a floating floor is made from it, or it is placed on a subfloor along joists, why is high bending strength needed? More important is the tendency to delamination and warping, and these are precisely the problems of plywood. In general, it’s up to you to decide which is better - plywood or OSB. Below is information to help you make an informed decision.
The comparison is given in points and it is difficult to judge objectivity, but...
Moisture resistance and environmental friendliness
Oddly enough, moisture resistance is directly related to environmental safety. The fact is that in the production of materials a synthetic binder is used, and it is possible to say which is more environmentally friendly - OSB or plywood, specifically for each material. Although, generally speaking, plywood is safer: there are brands that use safe substances in their production. But not all. For example, FSF is one of the cheapest types. It is made using a phenol-formaldehyde binder. So this brand is no different from OSB in terms of environmental friendliness.
The most reliable test carried out independently with materials intended for purchase
In the case of oriented strand board, phenolic resins are always used. They give the material high strength and moisture resistance. But it is phenol that is dangerous to health. Its release is controlled by the sanitation station. A special classification has been introduced - formaldehyde emissions. Each batch must be checked and, based on the measurement results, an emission class must be assigned. Safe ones are E0 or E1. And E2 and E3 can only be used outdoors. By the way, the same characteristic should be indicated in the technical parameters for FSF plywood.
Water resistance of OSB
Oriented strand boards are available in four water resistance categories:
- OSB1 and OSB2 - not moisture resistant, for use in rooms with normal operating conditions;
- OSB3 and OSB4 - waterproof, for use in conditions of high humidity.
Making a choice - plywood or OSB is not easy
If they are making a floor, they usually use OSB3. Its water resistance is sufficient for use in any floor pie, so the material is universal. If significant strength is required, you can take a higher grade.
Waterproof types of plywood
With plywood it's a little more complicated. In its production, various glues are used and it is this that affects the properties of the material. The following types are used in construction:
- FC - on urea glue. Good environmental performance, but moisture resistance is average. If you lay it on the floor, then in dry rooms where access to moisture is unlikely. There is waterproof plywood of this brand. The marking has added the letter B - FKV, sometimes the letter G is added - waterproof. But moisture resistance is achieved not through glue, but through wood additives/impregnations.
- FSF - on phenolic glue. This type has high moisture resistance, but phenolic glue releases formaldehyde. So you need to be sure that the material is safe. This is one of the cheapest types, often called construction. They are used more often for temporary structures - formwork.
- FKM - on melamine glue. Waterproof, but expensive.
- FB - bakelite with a water-soluble composition, BS - with alcohol-soluble glue. BS plywood is most often called aviation plywood. Light and durable, waterproof, expensive. The FB subtype is used more often in the construction of ships and railway cars, where the weight requirements are lower.
So it’s difficult to compare plywood and OSB in terms of water resistance. There are different brands and it’s a matter of specific choice. It’s just that in terms of water resistance, OSB is more reliable, since the wood chips are in a layer of glue that simply does not allow moisture to pass through to the wood. With plywood it is more complicated: the outer layers are wood veneer, and the veneer cuts along the edges of the sheet also remain open. So even moisture-resistant plywood often begins to warp - the top/bottom layer swells and the edges swell.
What is better to choose for the floor: plywood, chipboard or OSB?
Plywood, OSB boards and chipboard are very similar materials used for the same purposes, the main of which is flooring. When a person is faced with a renovation, he has a question about which of these materials to choose.
All these 3 materials have earned the trust of consumers and builders and have their own advantages and disadvantages.
First, let's take a closer look at these materials.
Oriented strand board (OSB, English oriented strand board, OSB) is a multilayer (3-4 or more layers) sheet consisting of wood chips (thin chips) glued together with various resins with the addition of synthetic wax and boric acid. The chips in the layers of the slab have an orientation: longitudinal in the outer layers, transverse in the inner layers.
Chipboard (official abbreviation - DSTP, unofficial - chipboard) is a sheet composite material made by hot pressing of wood particles, mainly chips, mixed with a binder of non-mineral origin with the introduction, if necessary, of special additives on single- and multi-story periodic presses or in continuous belt, track or extrusion units.
Plywood (laminated wood board) is a multilayer building material made by gluing together specially prepared veneer. The number of veneer layers is usually odd, from 3 or more. To increase the strength of plywood, layers of veneer are applied so that the wood fibers are strictly perpendicular to the previous sheet.
Advantages of plywood:
- Plywood can be used both as a finished floor and as a rough base for parquet, laminate and linoleum
- Plywood is much more aesthetically pleasing than chipboard (which, however, is not so important when installing a subfloor)
- The moisture resistance of plywood exceeds that of chipboard; it hardly wears out and is less likely to deform.
- Plywood, after slight wetting, will be able to return to its original shape, unlike chipboard.
Advantages of particle board (chipboard):
- It is an ideal layer for parquet and synthetic flooring.
- The price of chipboard is slightly lower than that of plywood
- Chipboard is easier to install
- The sound insulation and heat insulation qualities of chipboard are higher than those of plywood
Disadvantages of chipboard and plywood:
- Water that gets onto chipboard and plywood can deform them and cause the material to rot, which will ultimately negatively affect the quality of the finish.
- Both materials contain formaldehyde, which negatively affects the environmental friendliness of the home.
Let's compare plywood and chipboard with OSB boards:
- OSB or plywood
OSB is much cheaper than plywood, but unlike it, it cannot be used as a finished floor due to its completely unaesthetic appearance. At the moment, OSB boards are gradually replacing plywood from the construction market. They have relatively high moisture resistance, strength, and are easy to process.
Both materials are made from compressed shavings glued together with synthetic resins. But there are two significant differences in their production technology:
- In OSB, the length of the chips is quite large and reaches 15 cm; in chipboard, absolutely everything is used, including sawdust.
- In chipboard, the chips are placed haphazardly, unlike OSB, where the chips are arranged layer by layer and perpendicular to each other.
These two points give OSB advantages in strength at relatively similar prices.
How to choose?
Of all three materials, OSB is considered the most environmentally friendly, although it all depends on the manufacturing technology.
Each material is endowed with certain qualities, and the choice depends on your needs and capabilities.
If it is important to you:
- environmental friendliness and durability - purchase OSB;
- ease of installation, heat and sound insulation qualities - chipboard;
- aesthetics and moisture resistance - plywood.
build-74.ru
Oriented Strand Board Dimensions
Since OSB boards have different purposes, different sizes may be convenient. The situation with the sizes of OSB boards is not simple. 1220*2440 mm and 1250*2500 mm are always on sale. There are also formats 1250*2800 mm, 1250*3000 mm, 1200*6000 mm, but they are extremely rare in our market, although in many cases they are much more convenient to use. By choosing the right size, you get rid of the need to “grow” the missing centimeters or saw off the extra ones. But there are not many of them on the market, since these are imported slabs, and importing is difficult now...
The OSB board can be of different thicknesses - 9 mm, 12 mm, 15 mm, 18 mm, 22 mm, 25 mm. Each type of use has its own thickness:
- Wall and ceiling cladding - from 9 mm.
- Continuous sheathing for roofing materials - from 12 mm.
- An OSB board of 15 mm thickness will be used on the floor.
OSB board is a convenient building material. You can cut it with a regular wood saw, use a grinder with a cutting disc, or use a jigsaw. The material drills well; screw nails can be used without pre-drilling. But then their hats stick out, which is not always convenient.
Before finishing, the OSB board is coated with a primer. It is selected depending on the finishing materials - to equalize absorbency and improve adhesion to other materials.
Chipboard - characteristics and purpose
The production of chipboards or chipboards is based on pressing technology with sequential heating. The main raw materials for production are sawdust from coniferous and deciduous trees. After cleaning and grinding to the required fraction, the sawdust is mixed with an adhesive composition and, after forming a homogeneous mass, goes into a pressing-drying machine. This is where the formation of particle board occurs.
Under a hot press, a texture is formed in which the sawdust of the outer layers forms a monolithic dense layer, and the inner one has a looser consistency due to the unstructured arrangement of the sawdust. After drying at a temperature of about 190 degrees, the material is able to withstand heavy loads and is used as a basis for the manufacture of furniture, the construction of partitions and for the decorative design of premises.
The advantage of such a chipboard sheet is its density. The industry produces different sizes of slabs, the thickest having a thickness of 50 mm. Chipboards are easy to saw with a hand and electric saw. When processed, like natural wood, it can be sanded, milled, impregnated with impregnations, applied with a decorative coating and painted.
The smooth surface of the sheet allows you to make figures of different shapes from it; unlike wood, it does not have fibers oriented in a certain direction. But on the other hand, unlike wood, chipboard slabs are not able to withstand the load that boards of such thickness can withstand.
The range of particle boards includes boards for different purposes:
- Unpolished slabs;
- Sanded chipboard;
- Laminated chipboard;
- Chipboard is waterproof.
They vary in density and water resistance. During installation, fastening is carried out using the adhesive method, using self-tapping screws, screws, nails and furniture bolts.
The disadvantages of the material include poor water resistance, the impossibility of reusable use for installation in construction - holes for fastenings must be made in another place.
What is chipboard
This board is made from small shavings and sawdust, which are combined with resins by hot pressing. Residues and sawdust from wood processing enterprises are used for production. In a word – wood waste. The result is a universal and inexpensive sheet material. If chipboard is covered with a laminated film, the result is laminated chipboard - a more expensive material with a presentable appearance. Laminated chipboard is usually used for the manufacture of cabinet furniture in the mid-price category.
Chipboard is classified according to its quality characteristics:
- I or II Grade (depending on the quality of the material and the evenness of the surface;
- Number of layers from 1 to several;
- Degree of strength and moisture resistance;
- Surface type – polished and unpolished;
- Presence of toxic resins.
Application of chipboard
- Formwork;
- Construction of partitions and structures;
- Wall cladding;
- Arrangement of floors before laying the main covering (leveling);
- Furniture manufacturing;
- Manufacturing of doors, window sills;
- Construction of temporary technical structures.
All about OSB and chipboard
The main advantage of oriented strand boards (OSB) is strength and resistance to external factors, and the main advantage of particle boards (chipboards) is low cost.
On the picture:
Similarities and differences between OSB and chipboard
What is chipboard?
Particle boards are a material that is made from wood chips, sawdust, small particles of wood and synthetic resins using hot pressing.
What is OSB?
Oriented strand boards are produced by gluing wood fibers arranged in a special way under temperature and pressure. The binder in OSB is synthetic resins. The most suitable wood for the production of such boards in Russia is aspen.
On the picture:
What is the difference?
At first glance, the composition and production technology of the plates are similar. But OSB board is a more durable and flexible material, due to three or four layers of wood components. In the two outer layers the arrangement of fibers and chips is parallel to the length of the slab, while in the inner layers it is perpendicular.
You should try to attach particle boards the first time, because... the structure of the material is not dense enough for secondary connection. Re-attaching the slabs is not recommended, since the structure may not be tight enough.
In the photo: OSB 2 board from EGGER.
Particle boards are inferior in many respects: they are deformed from moisture and other external influences, and their structure is much less dense. However, the cost of chipboard is significantly lower than the cost of OSB, which largely compensates for other disadvantages.
Advantages of slabs compared to wood.
If we compare OSB and chipboard with wood, the advantages include the uniformity of the structure, the absence of knots and voids, and easier processing. In addition, the boards are protected from insects, and waterproof - from moisture. Most varnishes, paints and other materials suitable for wood are also suitable for OSB or chipboard. In general, the appearance of the slabs, with a high-quality finishing, is not inferior to wood; the OSB photo is the best confirmation of this.
Application of OSB and chipboard
Oriented strand boards.
Leveling floors, cladding walls, ceilings, installing walls and partitions - the use of OSB is truly multifaceted.
Due to their physical and mechanical characteristics, oriented particle boards are used not only for rough cladding, but also for the construction of walls, for continuous roof sheathing and in the manufacture of thermal panels, as a rigid base. In general, reviews of OSB board as a multifunctional material can only be very positive.
On the picture:
Particle boards.
Chipboard is also used in quite a variety of ways: for leveling almost any surface - walls, ceilings, floors, as well as for constructing window sills and partitions.
In addition, particle boards are very widely used for the manufacture of furniture: the low cost of the material is a key advantage compared to analogues.
On the picture:
Environmental friendliness of OSB and chipboard.
Unfortunately, due to the release of formaldehyde, oriented particle boards and particle boards cannot be called environmentally friendly materials. Currently, slabs with emission class E0 (i.e., harmless) are also produced, but the high costs of such production also affect the final cost of the slabs.
Images used in this article: kronospan.ru, egger.com
www.4living.ru
Material classification
Sheets of OSB boards have standard overall dimensions: length - 2500 millimeters, width - 1250 millimeters, thickness - 9; 12; 15; 18; 22 millimeters.
According to technical characteristics, products can be divided into 4 groups:
- OSB - 1 is a material with the lowest density, strength and moisture resistance. Similar slabs are used to make furniture.
- OSB-2 - products of the second class are recommended for indoor use. Such slabs can be used to construct interior partitions.
- OSB-3 indicates a material that is resistant to mechanical damage and moisture and is used for a wide variety of purposes.
- OSB-4 is considered the most dense and durable products. They can be used in conditions of high humidity, for example, for wall cladding in the bathroom. In addition, the panels are used for roofing and floor leveling. The slabs are often stitched together and used as floor beams.